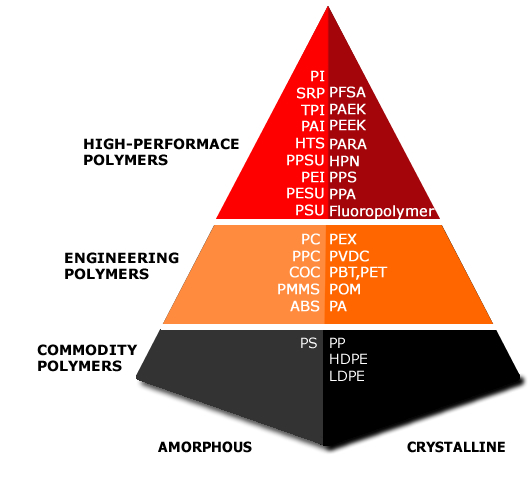
![]() High Performance polymers are characterised by their superlative mechanical, chemical and thermal properties. Polymer types include Fluoropolymers, high-performance Polyamides, Polyketones and Polyphenylene Sulphide. Demand for high-performance polymers tends to be driven by new product development and innovation; as well as by regulatory controls (for example ATEX).
High Performance polymers are characterised by their superlative mechanical, chemical and thermal properties. Polymer types include Fluoropolymers, high-performance Polyamides, Polyketones and Polyphenylene Sulphide. Demand for high-performance polymers tends to be driven by new product development and innovation; as well as by regulatory controls (for example ATEX).
![]() Engineering polymers have a structure that is random when liquid but becomes organized into crystalline groups when solid. They have a sharp melting point and have excellent mechanical properties such as stiffness and strength. These resins have high preformance in tough applications when compared to non-engineering resins.
Engineering polymers have a structure that is random when liquid but becomes organized into crystalline groups when solid. They have a sharp melting point and have excellent mechanical properties such as stiffness and strength. These resins have high preformance in tough applications when compared to non-engineering resins.
![]() Commodity polymers generally exhibit lower mechanical properties, but are typically lower in cost compared to engineering polymers. They are used in a wide and diverse range of products, for example polythene bags (polyethylene), vacuum-formed food packaging (low density polyethylene) and disposable drinking cups (high impact polystyrene).
Commodity polymers generally exhibit lower mechanical properties, but are typically lower in cost compared to engineering polymers. They are used in a wide and diverse range of products, for example polythene bags (polyethylene), vacuum-formed food packaging (low density polyethylene) and disposable drinking cups (high impact polystyrene).


